Menu
Menu
Many Americans experience vein problems in their legs, especially as they age or spend long hours standing. Conditions like spider veins, varicose veins, venous insufficiency, and venous ulcers are not only cosmetic—they can lead to discomfort and long-term complications. Fortunately, fantastic modern treatments such as venous ablation and sclerotherapy offer effective, minimally invasive solutions.
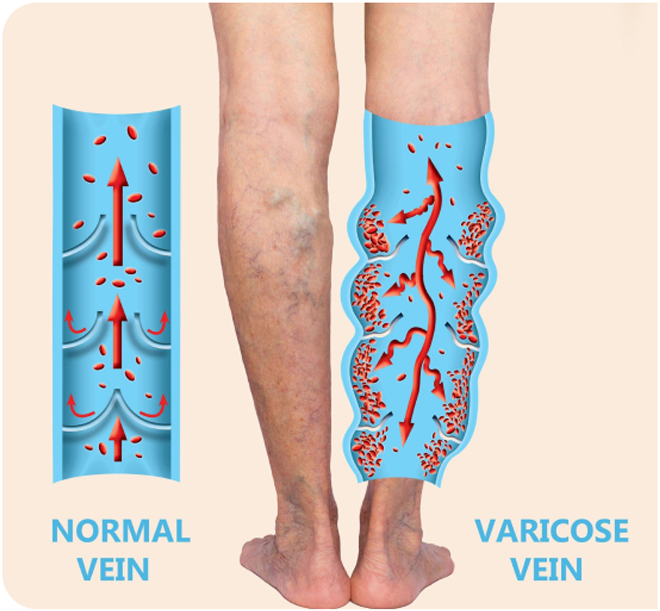
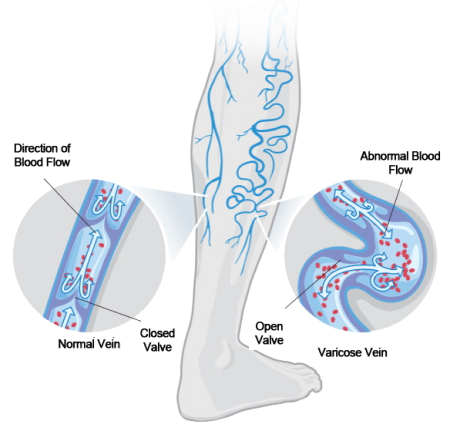
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) occurs when the valves in the leg veins don’t function properly, causing blood to flow backward and pool in the legs. This often leads to swelling, heaviness, aching, and sometimes skin changes.
Early treatment prevents the progression to more serious complications like skin ulcers.
Spider veins are tiny, red or blue veins just under the skin, often appearing on the thighs, calves, or ankles. They’re typically harmless but may indicate mild venous insufficiency.
Reticular veins are slightly larger than spider veins, bluish in color, and located deeper under the skin. They often serve as feeder veins to spider veins and may form networks on the thighs or behind the knees.
They are not usually painful but may worsen over time and contribute to visible vein clusters.
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that rise above the skin’s surface—usually on the legs. They are caused by faulty valves in the veins that allow blood to pool and stretch the vessel walls.
Symptoms may include:
Venous ulcers are open sores that usually develop near the ankles in people with advanced chronic venous insufficiency. They form when long-standing vein pressure damages the skin and underlying tissue.
Venous ulcers can be slow to heal and prone to infection.
Venous ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins. A catheter delivers heat energy (via laser or radiofrequency) inside the vein, sealing it shut.
It’s often used when symptoms are more than cosmetic or if ulcers or skin damage are present.
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a solution into the vein, causing it to scar, collapse, and eventually disappear. It’s most effective for spider veins and reticular veins, and sometimes for smaller varicose veins.
Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy can also target deeper veins when necessary.
Vein conditions are common, especially as we age or lead sedentary lives. Whether you’re dealing with cosmetic spider veins or painful ulcers, early evaluation and treatment can improve your quality of life and prevent serious complications.
Venous ablation and sclerotherapy are safe, proven treatments that target the root of the problem—not just the symptoms.
If you’re experiencing any of the issues above, talk to a vein specialist to explore the best treatment options for you.
Our clinic provides comprehensive cardiac care, from acute treatment to ongoing follow-up, for patients throughout the greater Hudson Valley. Schedule an appointment with our team through our convenient online scheduling form or by calling 877-EPIC-DOC (877-3742-362).
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your cardiologist or healthcare provider for personalized diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies for heart failure.
Epic Heart And Vascular Care is a Leading Vein Clinic that specializes in the treatment of Varicose Veins, Spider Veins, and other vein disorders. We offer a wide range of minimally invasive treatments that can help you get rid of your unwanted veins and improve your overall health and appearance.
Our team of experienced and board-certified vein specialists is committed to providing you with the highest quality care possible. We will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
Our vein treatments are safe, effective, and virtually painless. Most of our procedures can be done in our office in less than an hour, and you will be able to go home the same day.
This is a minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to close off varicose veins.
This procedure uses radiofrequency energy to close off varicose veins.
This procedure involves injecting a solution into varicose veins to cause them to collapse and disappear.
Filter through patient testimonials and experiences of RB health.
1353 Total Reviews

Your heart deserves the best care, contact us now to book your appointment and prioritize your well-being!